Cisco Catalyst 3750 is next-generation energy-efficient Layer
3 Fast Ethernet stackable switches while 3750X is layer 3 GE switches. The
Cisco Catalyst 3750 v2 Series consumes less power than its predecessors 3750.
The 3750-X Series Switches are enterprise-class lines of stackable and
standalone switches with StackWise Plus technology, they are the replacement of
Cisco 3750G and 3750E switches. Here are some commands on Cisco 3750 switches
for your reference.
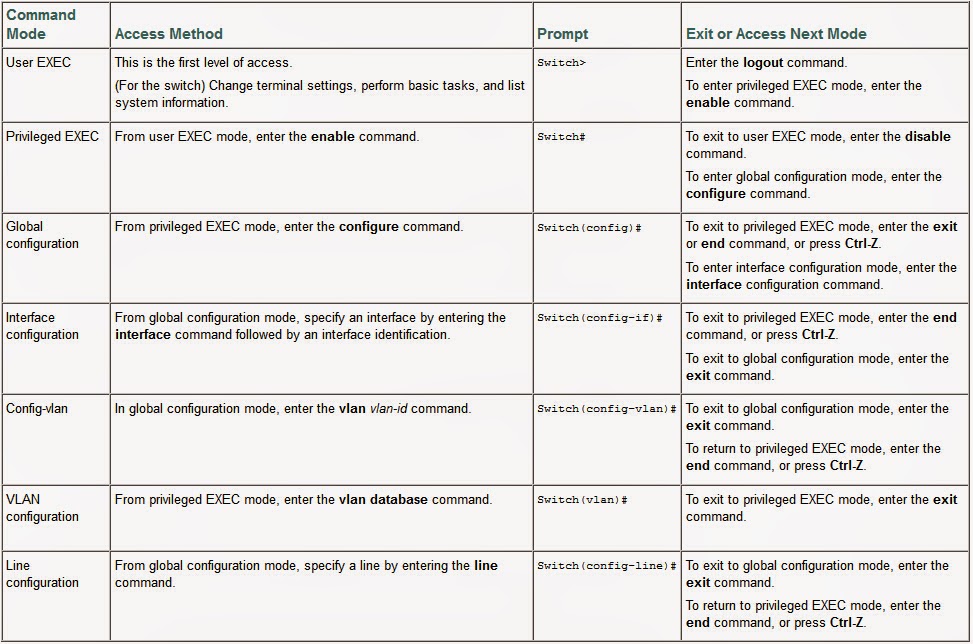
CLI Command Modes
This section describes the CLI command mode structure. Command modes support specific
Cisco IOS commands. For example, the interface interface-id command only
works when entered in global configuration mode.
The below table lists the main command modes, how to access each
mode, the prompt you see in that mode, and how to exit that mode. The prompts
listed use the default name Switch.
User EXEC Mode
After you access
the device, you are automatically in user EXEC command mode. The EXEC commands
available at the user level are a subset of those available at the privileged
level. In general, use the user EXEC commands to temporarily change terminal
settings, perform basic tests, and list system information.
The supported
commands can vary depending on the version of software in use. To display a
comprehensive list of commands, enter a question mark (?) at the prompt.
Privileged EXEC Mode
Because many of
the privileged commands configure operating parameters, privileged access
should be password-protected to prevent unauthorized use. The privileged
command set includes those commands contained in user EXEC mode, as well as the
configure privileged EXEC command through which you access the remaining
command modes.
If your system
administrator has set a password, you are prompted to enter it before being
granted access to privileged EXEC mode. The password does not appear on the screen
and is case sensitive.
The supported
commands can vary depending on the version of software in use. To display a
comprehensive list of commands, enter a question mark (?) at the prompt.
Global Configuration Mode
Global
configuration commands apply to features that affect the device as a whole. Use
the configure privileged EXEC command to enter global configuration mode. The
default is to enter commands from the management console.
When you enter the
configure command, a message prompts you for the source of the configuration
commands:
The supported
commands can vary depending on the version of software in use. To display a
comprehensive list of commands, enter a question mark (?) at the prompt.
To exit global
configuration command mode and to return to privileged EXEC mode, enter the end
or exit command, or press Ctrl-Z.
Interface Configuration Mode
Interface
configuration commands modify the operation of the interface. Interface
configuration commands always follow a global configuration command, which
defines the interface type.
Use the interface
interface-id command to access interface configuration mode. The new prompt
means interface configuration mode.
The supported
commands can vary depending on the version of software in use. To display a
comprehensive list of commands, enter a question mark (?) at the prompt.
To exit interface
configuration mode and to return to global configuration mode, enter the exit
command. To exit interface configuration mode and to return to privileged EXEC
mode, enter the end command, or press Ctrl-Z.
config-vlan Mode
Use this mode to
configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) or, when VTP mode is
transparent, to configure extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). When
VTP mode is transparent, the VLAN and VTP configuration is saved in the running
configuration file, and you can save it to the switch startup configuration
file by using the copy running-config startup-config privileged EXEC command.
The configurations of VLAN IDs 1 to 1005 are saved in the VLAN database if VTP
is in transparent or server mode. The extended-range VLAN configurations are
not saved in the VLAN database.
The supported
keywords can vary but are similar to the commands available in VLAN
configuration mode. To display a comprehensive list of commands, enter a
question mark (?) at the prompt.
For extended-range
VLANs, all characteristics except the MTU size must remain at the default
setting.
To return to
global configuration mode, enter exit; to return to privileged EXEC mode, enter
end. All the commands except shutdown take effect when you exit config-vlan
mode.
VLAN Configuration Mode
You can use the
VLAN configuration commands to create or modify VLAN parameters for VLAN IDs 1
to 1005.
The supported
commands can vary depending on the version of software in use. To display a
comprehensive list of commands, enter a question mark (?) at the prompt.
To return to
privileged EXEC mode, enter the abort VLAN configuration command to abandon the
proposed database. Otherwise, enter exit to implement the proposed new VLAN
database and to return to privileged EXEC mode. When you enter exit or apply,
the configuration is saved in the VLAN database; configuration from VLAN
configuration mode cannot be saved in the switch configuration file.
Line Configuration Mode
Line configuration
commands modify the operation of a terminal line. Line configuration commands
always follow a line command, which defines a line number. Use these commands
to change terminal parameter settings line-by-line or for a range of lines.
Use the line vty
line_number [ending_line_number] command to enter line configuration mode. The
new prompt means line configuration mode. The following example shows how to
enter line configuration mode for virtual terminal line 7:
The supported
commands can vary depending on the version of software in use. To display a
comprehensive list of commands, enter a question mark (?) at the prompt.
To exit line
configuration mode and to return to global configuration mode, use the exit
command. To exit line configuration mode and to return to privileged EXEC mode,
enter the end command, or press Ctrl-Z.